#operatingsystem learn through Kannada ಕನ್ನಡ ಭಾಷೆಯಲ್ಲಿ
#operatingsystem learn through Kannada ಕನ್ನಡ ಭಾಷೆಯಲ್ಲಿ
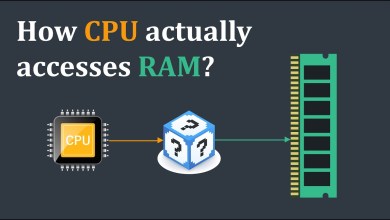
An operating system (OS) is a software program that acts as an intermediary between computer hardware and the software applications running on a computer. It manages and controls various hardware resources and provides services that allow software applications to interact with the hardware efficiently and effectively. In essence, an operating system is the core software that enables a computer to function and perform tasks.
Here are some of the key functions and roles of an operating system:
Resource Management: The operating system manages computer hardware resources such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, disk storage, input/output devices (keyboard, mouse, printer), and network connections. It allocates resources to different applications and ensures that they run smoothly without conflicting with each other.
Process Management: An OS allows multiple processes (programs or tasks) to run concurrently on a computer. It manages the scheduling of processes, ensuring that each process gets a fair share of the CPU time and resources.
Memory Management: The OS oversees the allocation and management of computer memory. It keeps track of which parts of memory are in use, allocates memory to processes, and ensures efficient memory usage to prevent memory-related errors.
File System Management: The operating system handles file and directory management on storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and removable media. It organizes and manages files, enabling users and applications to store, retrieve, and manipulate data.
User Interface: The OS provides a user interface that allows users to interact with the computer. This interface can be command-line based (text) or graphical, providing a visual way to interact with the computer through windows, icons, menus, and buttons.
Device Management: The OS manages communication with hardware devices such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices. It provides device drivers to facilitate proper communication between software and hardware components.
Security and Access Control: An operating system ensures the security and integrity of data and resources. It controls access to the system and its files through user accounts, passwords, permissions, and encryption mechanisms.
Networking: For computers connected to a network, the OS facilitates network communication. It manages network connections, protocols, and data transmission between devices.
Error Handling and Recovery: The OS monitors system operations for errors and malfunctions. It can detect errors, take corrective actions, and initiate system recovery procedures if necessary.
Virtualization: Many modern operating systems support virtualization, allowing a single physical computer to host multiple virtual machines, each running its own OS and applications.
Common examples of operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS (Apple), Linux, Unix, and various mobile operating systems like Android and iOS. The choice of an operating system depends on the type of computer or device and the intended use, as each OS has its own features, advantages, and limitations.
#OperatingSystem
#OS
#TechOS
#ComputerSoftware
#SystemManagement
#TechInfrastructure
#OSBasics
#TechKnowledge
#OperatingSystem101
#SoftwareEngineering
#TechFoundation
#SystemResources
#ComputerManagement
#TechBehindTheScenes
#ITInfrastructure
#operatingsystem learn through Kannada ಕನ್ನಡ ಭಾಷೆಯಲ್ಲಿ
[ad_2]
source