How an OS can maximise the use of resources | AL | By ZAK
From a technical perspective, the way an operating system (OS) maximizes the use of resources involves several key strategies and mechanisms. These include:
1. Resource Allocation and Management: The OS is responsible for allocating resources such as CPU time, memory space, and I/O devices to various processes. It uses scheduling algorithms for CPUs (like Round Robin, Priority Scheduling) and techniques like paging and segmentation for memory management to ensure efficient utilization.
2. Multi-Tasking and Process Management: The OS enables multi-tasking, allowing multiple processes to run simultaneously. This is achieved through context switching, where the state of a process is saved so the system can switch between processes, giving the illusion that they are running simultaneously.
3. Concurrency and Parallelism: By managing multiple threads within a process and using multi-core processors, the OS can perform parallel processing. This significantly increases the efficiency and speed of computational tasks.
4. I/O Management and Buffering: The OS optimizes the use of I/O devices through buffering, caching, and spooling. These techniques help in managing data transmission speeds between the processor and the I/O devices, ensuring that slower devices don’t bottleneck the system performance.
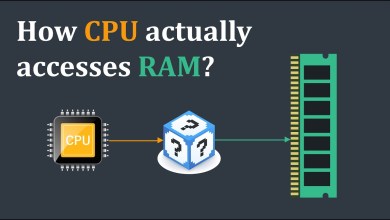
5. Memory Management: The OS optimizes RAM use through virtual memory management, allowing the system to use disk space as an extension of RAM. Techniques like demand paging and memory swapping help keep the system running efficiently even with limited physical memory.
6. Resource Monitoring and Optimization: Modern operating systems continuously monitor resource usage and can adjust priorities and allocations based on real-time demands. This dynamic resource management helps in maximizing the use of hardware capabilities.
7. Energy Efficiency: Especially in mobile and embedded systems, the OS plays a crucial role in managing the energy consumption of different hardware components, balancing performance with power-saving modes.
8. Security and Access Control: By managing user permissions and access rights, the OS ensures that resources are not misused or overused by unauthorized users or processes, maintaining system stability and security.
9. Driver and Hardware Compatibility: The OS ensures that all hardware components are properly utilized by using drivers that are optimized for those components. This ensures that the hardware resources are fully and efficiently utilized.
10. Load Balancing and Virtualization: In server and cloud environments, the OS may use load balancing and virtualization to distribute workloads evenly across multiple machines or virtual environments, maximizing the use of physical resources.
Each of these strategies is integral to how an operating system manages and maximizes the use of the computer’s hardware and software resources, ensuring optimal performance, stability, and efficiency.
[ad_2]
source